4.18 Recommended boundary conditions
This chapter covers a range of boundary conditions and their implementations. It first describes a specification of the basic conditions at inlet, outlet and wall boundaries for subsonic flow with fixed value and zero gradient.
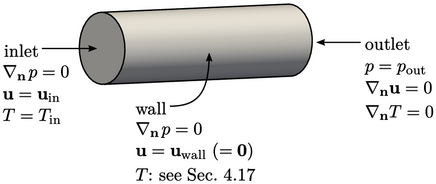
The conditions, based on the propagation of disturbances, are described in Sec. 4.3 :
- zero gradient on
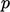 at an inlet, fixed
value on other variables;
at an inlet, fixed
value on other variables; - fixed value on
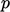 at an outlet, zero
gradient on other variables.
at an outlet, zero
gradient on other variables.
The conditions at a wall are similar to an
inlet for 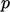 and
and 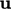 , but generally are represented more directly by
physical models, e.g. the
condition for heat flux
, but generally are represented more directly by
physical models, e.g. the
condition for heat flux 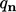 for
for 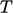 .
.
Supersonic conditions
The basic conditions for supersonic flow are discussed in
Sec. 4.5
. If the flow speed is
supersonic at an inlet, the basic condition is fixed value for
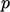 ;
it is zero gradient for
;
it is zero gradient for 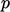 if the flow is supersonic at an outlet.
if the flow is supersonic at an outlet.
Robust, practical conditions
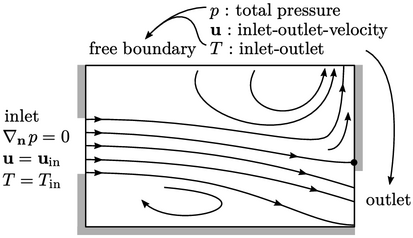
Section 4.6 introduced a free boundary that cannot be defined as an inlet or outlet, but instead often uses the following conditions:
- total
pressure for
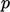 , see Sec. 4.7
;
, see Sec. 4.7
; - inlet-outlet-velocity for
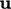 , see
Sec. 4.15
;
, see
Sec. 4.15
; - inlet-outlet for
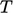 , see
Sec. 4.10.
, see
Sec. 4.10.
These conditions also respond well at an outlet, in the event that some inflow occurs at startup, a rotating structure passes through the boundary etc., see Sec. 4.10 .
The freestream conditions,
Sec. 4.16,
are effective for cases with known 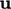 and
and 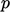 at a free,
far-field boundary.
at a free,
far-field boundary.
The symmetry and wedge conditions enable suitable cases to be simplified as symmetric and axisymmetric, respectively.
In the presence of a body force 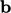 , the zero gradient
condition for
, the zero gradient
condition for 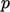 at inlets and walls should be replaced by a
fixed gradient condition
at inlets and walls should be replaced by a
fixed gradient condition
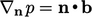 ,
see Sec. 4.4
.
,
see Sec. 4.4
.