8.8 Venturi tube
A Venturi tube is a device used to measure the flow rate of a fluid in a pipe. The device exploits the Venturi effect4, i.e. that pressure reduces when the fluid flows through a restriction.
The volumetric flow rate 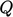 is calculated
according to
is calculated
according to
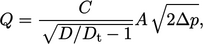 |
(8.2) |
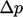 is the decrease in kinematic pressure
is the decrease in kinematic pressure 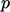 between the Venturi
inlet and throat;
between the Venturi
inlet and throat; 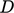 and
and 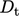 are the inlet and throat diameter,
respectively; the cross-sectional area is
are the inlet and throat diameter,
respectively; the cross-sectional area is 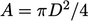 ; and,
; and, 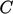 is a discharge coefficient. A coefficient of
is a discharge coefficient. A coefficient of  satisfies the Bernoulli
equation,
satisfies the Bernoulli
equation, 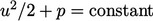 , between the inlet
and throat, where
, between the inlet
and throat, where 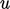 is the fluid speed.
is the fluid speed.
For 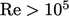 ,
, 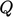 is calculated accurately using
is calculated accurately using 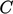 values between
0.97 and 1,5 but, for
values between
0.97 and 1,5 but, for 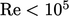 , suitable values of
, suitable values of
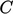 decrease significantly below 1 in order to account for pressure
losses due to viscous forces.
decrease significantly below 1 in order to account for pressure
losses due to viscous forces.
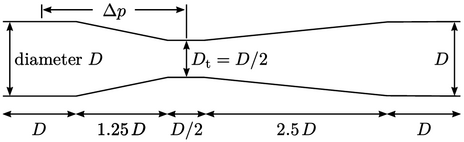
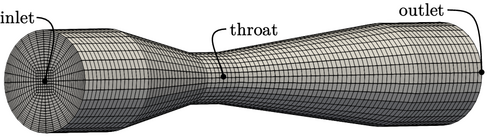
A simulation was performed to calculate
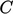 for a Venturi tube, shown in the figure, with
for a Venturi tube, shown in the figure, with 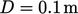 and an inlet
and an inlet
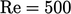 .
The inlet velocity was specified using the quadratic profile in
Sec. 8.7
with a mean
cross-sectional speed
.
The inlet velocity was specified using the quadratic profile in
Sec. 8.7
with a mean
cross-sectional speed 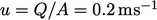 , corresponding to a maximum speed
, corresponding to a maximum speed 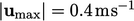 .
.
The simulation used the steady-state algorithm
in Sec. 5.12,
with an incompressible fluid with uniform 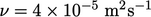 . The mesh contained
57,600 cells, with a near-wall cell height of 1.5mm, which resolved
the velocity profiles as shown below. The flow recirculates near the wall downstream of the Venturi throat,
causing inflow at the outlet boundary. Consequently, the total
pressure and inlet-outlet-velocity boundary conditions, described
in Sec. 4.7
and Sec. 4.15
respectively, were
applied at the outlet to maintain stability.
. The mesh contained
57,600 cells, with a near-wall cell height of 1.5mm, which resolved
the velocity profiles as shown below. The flow recirculates near the wall downstream of the Venturi throat,
causing inflow at the outlet boundary. Consequently, the total
pressure and inlet-outlet-velocity boundary conditions, described
in Sec. 4.7
and Sec. 4.15
respectively, were
applied at the outlet to maintain stability.
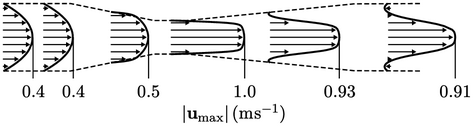
The flow was laminar so no turbulence modelling
was required. The solution converged to within an absolute
tolerance 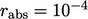 , see Sec. 5.4
, in 292 iterations.
, see Sec. 5.4
, in 292 iterations.
The pressure drop was 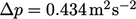 between the centres of
the inlet and throat sections, with a corresponding
between the centres of
the inlet and throat sections, with a corresponding 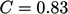 .
.