6.6 Scales of turbulence
In Sec. 6.2 , turbulence was pictured as a mass of intertwined eddies which are rotating and distorting. The rotation, i.e. vorticity, mostly originates at solid boundaries and propagates locally (Sec. 6.3 ) through boundary layers (Sec. 6.4 ), which can separate and shed into the flow field (Sec. 6.5 ).
Flow disturbances trigger instabilities which
cause vortices to stretch, compress and/or ‘break up’. At a
sufficiently high 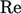 , coherent flow structures rapidly disintegrate into a
mass of turbulent eddies. This process is described in Richardson’s
poem:8
, coherent flow structures rapidly disintegrate into a
mass of turbulent eddies. This process is described in Richardson’s
poem:8
Big whorls have little whorls that feed off their velocity, and little whorls have lesser whorls and so on to viscosity — in the molecular sense.
In other words, large eddies created by instabilities become progressively smaller until they reach a size where the dissipation of their kinetic energy due to (molecular) viscosity is significant. The loss of kinetic energy causes these eddies to “die out” before they can become any smaller.
Kolmogorov microscales
The Kolmogorov
microscales9 describe the smallest scales that can exist in
turbulent flow. They can be derived from heuristic arguments as
follows. Energy dissipates as heat at a rate of 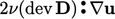 per unit mass,
obtained from Eq. (2.58
) and
switching from ‘per unit volume’ by replacing
per unit mass,
obtained from Eq. (2.58
) and
switching from ‘per unit volume’ by replacing 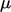 by
by  .
.
Using scale similarity arguments
(Sec. 2.21
) the average rate of
dissipation of energy 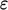 can then be estimated for the smallest scales,
characterised by length
can then be estimated for the smallest scales,
characterised by length 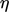 and speed
and speed  , to be
, to be
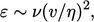 |
(6.7) |
 ” means ”of the order of
magnitude”.
” means ”of the order of
magnitude”.
Dissipation occurs when the Reynolds number,
based on the Kolmogorov scales, is of the order unity, i.e. 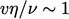 . Combined with
Eq. (6.7
) this yields the
Kolmogorov microscales below.
. Combined with
Eq. (6.7
) this yields the
Kolmogorov microscales below.
At the largest scales, eddies generated from the
mean flow can be characterised by a length 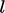 and flow speed
and flow speed
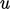 (of the scale of turbulent fluctuations). The kinetic energy per
unit mass of these eddies
(of the scale of turbulent fluctuations). The kinetic energy per
unit mass of these eddies 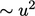 .
.
Experiments show the lifetime of an eddy is of
the order of the time for one revolution, the turn-over time 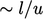 . Therefore the rate of
transfer of kinetic energy from larger to smaller eddies is
. Therefore the rate of
transfer of kinetic energy from larger to smaller eddies is
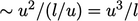 .
.
This rate of transfer of energy between scales
must match the rate of dissipation, Eq. (6.7).
Equating the two energy rates yields the correspondence between the
Kolmogorov scales and the largest scales in terms of a large scale
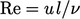 :
:
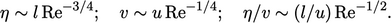 |
(6.9) |