[version 13][version 12][version 11][version 10][version 9][version 8][version 7][version 6]
3.2 Compiling applications and libraries
Compilation is an integral part of code development that requires careful management since every piece of code requires its own set instructions to access dependent components of the OpenFOAM library. In Linux systems there are various tools to help automate the management process, starting with the standard make utility. OpenFOAM uses its own wmake compilation script that is based on make. It is specifically designed for the large number of individual components that are compiled separately in OpenFOAM (approximately 150 applications and 150 libraries).
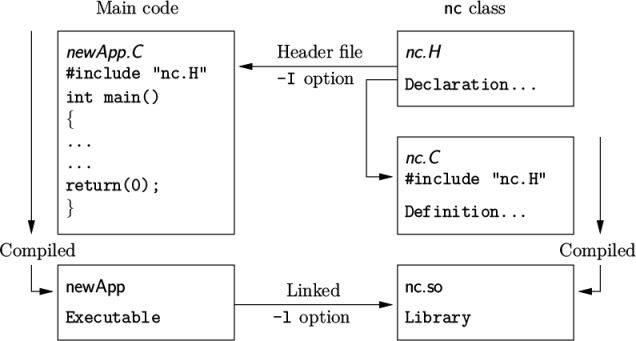
To understand the compilation process, we first need to explain certain aspects of C++ and its file structure, shown schematically in Figure 3.1 . A class is defined through a set of instructions such as object construction, data storage and class member functions. The file that defines these functions — the class definition — takes a .C extension, e.g. a class nc would be written in the file nc.C. This file can be compiled independently of other code into a binary executable library file known as a shared object library with the .so file extension, i.e.nc.so. When compiling a piece of code, say newApp.C, that uses the nc class, nc.C need not be recompiled, rather newApp.C calls the nc.so library at runtime. This is known as dynamic linking.
3.2.1 Header .H files
As a means of checking errors, the piece of code being compiled must know that the classes it uses and the operations they perform actually exist. Therefore each class requires a class declaration, contained in a header file with a .H file extension, e.g. nc.H, that includes the names of the class and its functions. This file is included at the beginning of any piece of code using the class, using the #include directive described below, including the class declaration code itself. Any piece of .C code can resource any number of classes and must begin by including all the .H files required to declare these classes. Those classes in turn can resource other classes and so also begin by including the relevant .H files. By searching recursively down the class hierarchy we can produce a complete list of header files for all the classes on which the top level .C code ultimately depends; these .H files are known as the dependencies. With a dependency list, a compiler can check whether the source files have been updated since their last compilation and selectively compile only those that need to be.
Header files are included in the code using the #include directive, e.g.
#include "otherHeader.H";
It is wmake that performs the task of maintaining file dependency lists amongst other functions listed below.
-
Automatic generation and maintenance of file dependency lists, i.e. lists of files which are included in the source files and hence on which they depend.
-
Multi-platform compilation and linkage, handled through appropriate directory structure.
-
Multi-language compilation and linkage, e.g. C, C++, Java.
-
Multi-option compilation and linkage, e.g. debug, optimised, parallel and profiling.
-
Support for source code generation programs, e.g. lex, yacc, IDL, MOC.
-
Simple syntax for source file lists.
-
Automatic creation of source file lists for new codes.
-
Simple handling of multiple shared or static libraries.
3.2.2 Compiling with wmake
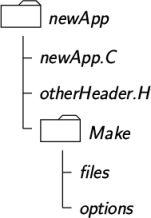
OpenFOAM applications are organised using a standard convention that the source code of each application is placed in a directory whose name is that of the application. The top level source file then takes the application name with the .C extension. For example, the source code for an application called newApp would reside is a directory newApp and the top level file would be newApp.C as shown in Figure 3.2 .
wmake then requires the directory must contain a Make subdirectory containing 2 files, options and files, that are described in the following sections.
3.2.3 Including headers
The compiler searches for the included header files in the following order, specified with the -I option in wmake:
-
the $WM_PROJECT_DIR/src/OpenFOAM/lnInclude directory;
-
a local lnInclude directory, i.e.newApp/lnInclude;
-
the local directory, i.e.newApp;
-
platform dependent paths set in files in the $WM_PROJECT_DIR/wmake/rules directory, e.g./usr/include/X11;
-
other directories specified explicitly in the Make/options file with the -I option.
The Make/options file contains the full directory paths to locate header files using the syntax:
EXE_INC = \
-I<directoryPath1> \
-I<directoryPath2> \
… \
-I<directoryPathN>
3.2.4 Linking to libraries
The compiler links to shared object library files in the following directory paths, specified with the -L option in wmake:
-
the $FOAM_LIBBIN directory;
-
platform dependent paths set in files in the $WM_DIR/rules directory, e.g.$(MPI_ARCH_PATH)/lib;
-
other directories specified in the Make/options file.
The actual library files to be linked must be specified using the -l option and removing the lib prefix and .so extension from the library file name, e.g. libnew.so is included with the flag -lnew. By default, wmake loads the following libraries:
-
the libOpenFOAM.so library from the $FOAM_LIBBIN directory;
-
platform dependent libraries specified in set in files in the $WM_DIR/rules directory, e.g. libm.so and libdl.so;
-
other libraries specified in the Make/options file.
The Make/options file contains the full directory paths and library names using the syntax:
EXE_LIBS = \
-L<libraryPath> \
-l<library1> \
-l<library2> \
… \
-l<libraryN>
3.2.5 Source files to be compiled
The compiler requires a list of .C source files that must be compiled. The list must contain the main .C file but also any other source files that are created for the specific application but are not included in a class library. For example, users may create a new class or some new functionality to an existing class for a particular application. The full list of .C source files must be included in the Make/files file. For many applications the list only includes the name of the main .C file, e.g. newApp.C in the case of our earlier example.
The Make/files file also includes a full path and name of the compiled executable, specified by the EXE = syntax. Standard convention stipulates the name is that of the application, i.e.newApp in our example. The OpenFOAM release offers two useful choices for path: standard release applications are stored in $FOAM_APPBIN; applications developed by the user are stored in $FOAM_USER_APPBIN.
If the user is developing their own applications, we recommend they create an applications subdirectory in their $WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR directory containing the source code for personal OpenFOAM applications. As with standard applications, the source code for each OpenFOAM application should be stored within its own directory. The only difference between a user application and one from the standard release is that the Make/files file should specify that the user’s executables are written into their $FOAM_USER_APPBIN directory. The Make/files file for our example would appear as follows:
newApp.C
EXE = $(FOAM_USER_APPBIN)/newApp
3.2.6 Running wmake
The wmake script is generally executed by typing:
wmake <optionalDirectory>
3.2.7 wmake environment variables
For information, the general environment variable settings used by wmake are listed below.
-
$WM_PROJECT_INST_DIR: full path to the installation directory, e.g.$HOME/OpenFOAM.
-
$WM_PROJECT: name of the project being compiled, i.e. OpenFOAM.
-
$WM_PROJECT_VERSION: version of the project being compiled, i.e. 12.
-
$WM_PROJECT_DIR: full path to the main directory of the OpenFOAM release, e.g. $HOME/OpenFOAM/OpenFOAM-12.
-
$WM_PROJECT_USER_DIR: full path to the equivalent directory for customised developments in the user account, e.g. $HOME/OpenFOAM/${USER}-12.
-
$WM_THIRD_PARTY_DIR: full path to the directory of ThirdParty software, e.g. $HOME/OpenFOAM/ThirdParty-12.
The environment variable settings for the compilation with wmake are listed below.
-
$WM_ARCH: machine architecture, e.g. linux, linux64, linuxArm64, linuxARM7, linuxPPC64, linuxPPC64le.
-
$WM_LINK_LANGUAGE: compiler used to link libraries and executables c++.
-
$WM_MPLIB: parallel communications library, SYSTEMOPENMPI = system version of openMPI, alternatives include OPENMPI, SYSTEMMPI, MPICH, MPICH-GM, HPMPI, MPI, QSMPI, INTELMPI and SGIMPI.
-
$WM_OPTIONS, e.g. linux64GccDPInt32Opt, formed by combining $WM_ARCH, $WM_COMPILER, $WM_PRECISION_OPTION, $WM_LABEL_OPTION, and $WM_COMPILE_OPTION.
-
$WM_PRECISION_OPTION: floating point precision of the compiled binares, SP = single precision, DP = double precision.
The environment variable settings relating to the choice of compiler and options withwmake are listed below.
-
$WM_CXXFLAGS: extra flags to the C++ compiler, e.g. -m64 -fPIC -std=c++0x.
-
$WM_COMPILER: compiler being used, e.g. Gcc = gcc, Clang = LLVM Clang
-
$WM_COMPILE_OPTION: compilation option, Debug = debugging, Opt = optimised.
-
$WM_COMPILER_LIB_ARCH: compiler library architecture, e.g. 64.
-
$WM_COMPILER_TYPE: choice of compiler, system, or ThirdParty, i.e. compiled in ThirdParty directory.
3.2.8 Removing dependency lists: wclean
When it is run, wmake builds a dependency list file with a .dep file extension, e.g. newApp.C.dep in our example, in a $WM_OPTIONS sub-directory of the Make directory, e.g. Make/linuxGccDPInt64Opt. If the user wishes to remove these files, e.g. after making code changes, the user can run the wclean script by typing:
wclean <optionalDirectory>
3.2.9 Compiling libraries
When compiling a library, there are 2 critical differences in the configuration of the file in the Make directory:
-
in the files file, EXE = is replaced by LIB = and the target directory for the compiled entity changes from $FOAM_APPBIN to $FOAM_LIBBIN (and an equivalent $FOAM_USER_LIBBIN directory);
-
in the options file, EXE_LIBS = is replaced by LIB_LIBS = to indicate libraries linked to library being compiled.
When wmake is executed it additionally creates a directory named lnInclude that contains soft links to all the files in the library. The lnInclude directory is deleted by the wclean script when cleaning library source code.
3.2.10 Compilation example: the foamRun application
The source code for application foamRun is in the $FOAM_SOLVERS/foamRun directory and the top level source file is named foamRun.C. The foamRun.C source code is:
1/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*\ 2 ========= | 3 \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox 4 \\ / O peration | Website: https://openfoam.org 5 \\ / A nd | Copyright (C) 2022-2023 OpenFOAM Foundation 6 \\/ M anipulation | 7------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8License 9 This file is part of OpenFOAM. 10 11 OpenFOAM is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it 12 under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by 13 the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or 14 (at your option) any later version. 15 16 OpenFOAM is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT 17 ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or 18 FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License 19 for more details. 20 21 You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License 22 along with OpenFOAM. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. 23 24Application 25 foamRun 26 27Description 28 Loads and executes an OpenFOAM solver module either specified by the 29 optional \c solver entry in the \c controlDict or as a command-line 30 argument. 31 32 Uses the flexible PIMPLE (PISO-SIMPLE) solution for time-resolved and 33 pseudo-transient and steady simulations. 34 35Usage 36 \b foamRun [OPTION] 37 38 - \par -solver <name> 39 Solver name 40 41 - \par -libs '(\"lib1.so\" ... \"libN.so\")' 42 Specify the additional libraries loaded 43 44 Example usage: 45 - To run a \c rhoPimpleFoam case by specifying the solver on the 46 command line: 47 \verbatim 48 foamRun -solver fluid 49 \endverbatim 50 51 - To update and run a \c rhoPimpleFoam case add the following entries to 52 the controlDict: 53 \verbatim 54 application foamRun; 55 56 solver fluid; 57 \endverbatim 58 then execute \c foamRun 59 60\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 61 62#include "argList.H" 63#include "solver.H" 64#include "pimpleSingleRegionControl.H" 65#include "setDeltaT.H" 66 67using namespace Foam; 68 69// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * // 70 71int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 72{ 73 argList::addOption 74 ( 75 "solver", 76 "name", 77 "Solver name" 78 ); 79 80 #include "setRootCase.H" 81 #include "createTime.H" 82 83 // Read the solverName from the optional solver entry in controlDict 84 word solverName 85 ( 86 runTime.controlDict().lookupOrDefault("solver", word::null) 87 ); 88 89 // Optionally reset the solver name from the -solver command-line argument 90 args.optionReadIfPresent("solver", solverName); 91 92 // Check the solverName has been set 93 if (solverName == word::null) 94 { 95 args.printUsage(); 96 97 FatalErrorIn(args.executable()) 98 << "solver not specified in the controlDict or on the command-line" 99 << exit(FatalError); 100 } 101 else 102 { 103 // Load the solver library 104 solver::load(solverName); 105 } 106 107 // Create the default single region mesh 108 #include "createMesh.H" 109 110 // Instantiate the selected solver 111 autoPtr<solver> solverPtr(solver::New(solverName, mesh)); 112 solver& solver = solverPtr(); 113 114 // Create the outer PIMPLE loop and control structure 115 pimpleSingleRegionControl pimple(solver.pimple); 116 117 // Set the initial time-step 118 setDeltaT(runTime, solver); 119 120 // * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * // 121 122 Info<< nl << "Starting time loop\n" << endl; 123 124 while (pimple.run(runTime)) 125 { 126 // Update PIMPLE outer-loop parameters if changed 127 pimple.read(); 128 129 solver.preSolve(); 130 131 // Adjust the time-step according to the solver maxDeltaT 132 adjustDeltaT(runTime, solver); 133 134 runTime++; 135 136 Info<< "Time = " << runTime.userTimeName() << nl << endl; 137 138 // PIMPLE corrector loop 139 while (pimple.loop()) 140 { 141 solver.moveMesh(); 142 solver.motionCorrector(); 143 solver.fvModels().correct(); 144 solver.prePredictor(); 145 solver.momentumPredictor(); 146 solver.thermophysicalPredictor(); 147 solver.pressureCorrector(); 148 solver.postCorrector(); 149 } 150 151 solver.postSolve(); 152 153 runTime.write(); 154 155 Info<< "ExecutionTime = " << runTime.elapsedCpuTime() << " s" 156 << " ClockTime = " << runTime.elapsedClockTime() << " s" 157 << nl << endl; 158 } 159 160 Info<< "End\n" << endl; 161 162 return 0; 163} 164 165 166// ************************************************************************* //
The code begins with a description of the application contained within comments over 1 line (//) and multiple lines (/*…*/). Following that, the code contains several # include statements, e.g. # include "argList.H", which causes the compiler to suspend reading from the current file, foamRun.C to read the argList.H file.
foamRun uses the finite volume numerics library and therefore requires the necessary header files, specified by the EXE_INC = -I… option, and links to the libraries with the EXE_LIBS = -l… option. The Make/options therefore contains the following:
1EXE_INC = \ 2 -I$(LIB_SRC)/finiteVolume/lnInclude 3 4EXE_LIBS = \ 5 -lfiniteVolume
foamRun contains the foamRun.C source and the executable is written to the $FOAM_APPBIN directory. The application uses functions to initialise and adjust the time step, defined in the setDeltaT.C file. The Make/files therefore contains:
1setDeltaT.C 2foamRun.C 3 4EXE = $(FOAM_APPBIN)/foamRun
Following the recommendations of section 3.2.5 , the user can compile a separate version of foamRun into their local $FOAM_USER_DIR directory as follows. First, the user should copy the foamRun source code to a local directory, e.g. $FOAM_RUN.
cd $FOAM_RUN
cp -r $FOAM_SOLVERS/foamRun .
cd foamRun
1foamRun.C 2 3EXE = $(FOAM_USER_APPBIN)/foamRun
Finally, they should run the wmake script.
wmake
Making dependency list for source file foamRun.C
g++ -std=c++14 -m64…
…
-o ... platforms/linux64GccDPInt32Opt/bin/foamRun
wclean
3.2.11 Debug messaging and optimisation switches
OpenFOAM provides a system of messaging that is written during runtime, most of which are to help debugging problems encountered during running of a OpenFOAM case. The switches are listed in the $WM_PROJECT_DIR/etc/controlDict file; should the user wish to change the settings they should make a copy to their $HOME directory, i.e. $HOME/.OpenFOAM/12/controlDict file (see section 4.3 for more information). The list of possible switches is extensive, relating to a class or range of functionality, and can be switched on by their inclusion in the controlDict file, and by being set to 1. For example, OpenFOAM can perform the checking of dimensional units in all calculations by setting the dimensionSet switch to 1.
A small number of switches control messaging at three levels, 0, 1 and 2, most notably the overall level switch and lduMatrix which provides messaging for solver convergence during a run.
There are some switches that control certain operational and optimisation issues. Of particular importance is fileModificationSkew. OpenFOAM scans the write time of data files to check for modification. When running over a NFS with some disparity in the clock settings on different machines, field data files appear to be modified ahead of time. This can cause a problem if OpenFOAM views the files as newly modified and attempting to re-read this data. The fileModificationSkew keyword is the time in seconds that OpenFOAM will subtract from the file write time when assessing whether the file has been newly modified. The main optimisation switches are listed below:
-
fileModificationSkew: a time in seconds that should be set higher than the maximum delay in NFS updates and clock difference for running OpenFOAM over a NFS.
-
fileModificationChecking: method of checking whether files have been modified during a simulation, either reading the timeStamp or using inotify; versions that read only master-node data also exist, termed timeStampMaster and inotifyMaster.
-
commsType: parallel communications type, nonBlocking, scheduled or blocking.
-
floatTransfer: if 1, will compact numbers to float precision before transfer; default is 0.
-
nProcsSimpleSum: optimises the global sum for parallel processing, by setting the number of processors above which a hierarchical sum is performed rather than a linear sum.
3.2.12 Dynamic linking at run-time
The situation may arise that a user creates a new library, say new1, and wishes the features within that library to be available across a range of applications. For example, the user may create a new boundary condition, compiled into new1, that would need to be recognised by a range of solver applications, pre- and post-processing utilities, mesh tools, etc. Under normal circumstances, the user would need to recompile every application with the new1 linked to it.
Instead there is a simple mechanism to link one or more shared object libraries dynamically at run-time in OpenFOAM. The use can simply add the optional keyword entry libs to the controlDict file for a case and enter the full names of the libraries within a list (as quoted string entries). For example, if a user wished to link the libraries new1 and new2 at run-time, they would simply need to add the following to the case controlDict file:
libs
(
"libnew1.so"
"libnew2.so"
);