[version 13][version 12][version 11][version 10][version 9][version 8][version 7][version 6]
4.2 Basic input/output file format
OpenFOAM needs to read a range of data structures such as strings, scalars, vectors, tensors, lists and fields. The input/output (I/O) format of files is designed to be extremely flexible to enable the user to modify the I/O in OpenFOAM applications as easily as possible. The I/O follows a simple set of rules that make the files extremely easy to understand, in contrast to many software packages whose file format may not only be difficult to understand intuitively but also not be published. The OpenFOAM file format is described in the following sections.
4.2.1 General syntax rules
The format follows some general principles of C++ source code.
- Files have free form, with no particular meaning assigned to any column and no need to indicate continuation across lines.
- Lines have no particular meaning except to a // comment delimiter which makes OpenFOAM ignore any text that follows it until the end of line.
- A comment over multiple lines is done by enclosing the text between /* and */ delimiters.
4.2.2 Dictionaries
OpenFOAM uses dictionaries as the most common means of specifying data. A dictionary is an entity that contains data entries that can be retrieved by the I/O by means of keywords. The keyword entries follow the general format
<keyword> <dataEntry1> … <dataEntryN>;
<keyword> <dataEntry>;
<dictionaryName>
{
… keyword entries …
}
4.2.3 The data file header
All data files that are read and written by OpenFOAM begin with a dictionary named FoamFile containing a standard set of keyword entries, listed in Table 4.1.
| Keyword | Description | Entry |
| I/O format version | 2.0 |
|
| Data format | ascii / binary |
|
| Path to the file, in "…" | (optional) |
|
| OpenFOAM class constructed from the data file concerned | typically dictionary or a field, e.g. volVectorField |
|
| Filename | e.g. controlDict |
|
The table provides brief descriptions of each entry, which is probably sufficient for most entries with the notable exception of class. The class entry is the name of the C++ class in the OpenFOAM library that will be constructed from the data in the file. Without knowledge of the underlying code which calls the file to be read, and knowledge of the OpenFOAM classes, the user will probably be unable to surmise the class entry correctly. However, most data files with simple keyword entries are read into an internal dictionary class and therefore the class entry is dictionary in those cases.
The following example shows the use of keywords to provide data for a case using the types of entry described so far. The extract, from an fvSolution dictionary file, contains 2 dictionaries, solvers and PISO. The solvers dictionary contains multiple data entries for solver and tolerances for each of the pressure and velocity equations, represented by the p and U keywords respectively; the PISO dictionary contains algorithm controls.
18 solvers
19 {
20 p
21 {
22 solver PCG;
23 preconditioner DIC;
24 tolerance 1e-06;
25 relTol 0.05;
26 }
27
28 pFinal
29 {
30 $p;
31 relTol 0;
32 }
33
34 U
35 {
36 solver smoothSolver;
37 smoother symGaussSeidel;
38 tolerance 1e-05;
39 relTol 0;
40 }
41 }
42
43 PISO
44 {
45 nCorrectors 2;
46 nNonOrthogonalCorrectors 0;
47 pRefCell 0;
48 pRefValue 0;
49 }
50
51
52 // ************************************************************************* //
4.2.4 Lists
OpenFOAM applications contain lists, e.g. a list of vertex coordinates for a mesh description. Lists are commonly found in I/O and have a format of their own in which the entries are contained within round braces ( ). There is also a choice of format preceeding the round braces:
- simple
- the keyword is followed immediately by round braces <listName>
(
… entries …
); - numbered
- the keyword is followed by the number of elements <n> in the list
<listName>
<n>
(
… entries …
); - token identifier
- the keyword is followed by a class name identifier Label<Type>
where <Type> states what the list contains, e.g. for a list of scalar elements
is <listName>
List<scalar>
<n> // optional
(
… entries …
);
Note that <scalar> in List<scalar> is not a generic name but the actual text that should be entered.
The simple format is a convenient way of writing a list. The other formats allow the code to read the data faster since the size of the list can be allocated to memory in advance of reading the data. The simple format is therefore preferred for short lists, where read time is minimal, and the other formats are preferred for long lists.
4.2.5 Scalars, vectors and tensors
A scalar is a single number represented as such in a data file. A vector is a
VectorSpace of rank 1 and dimension 3, and since the number of elements is
always fixed to 3, the simple List format is used. Therefore a vector 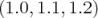 is written:
is written:
(1.0 1.1 1.2)
(
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
)
( 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 )
4.2.6 Dimensional units
In continuum mechanics, properties are represented in some chosen units,
e.g. mass in kilograms (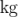 ), volume in cubic metres (
), volume in cubic metres (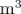 ), pressure in
Pascals (
), pressure in
Pascals (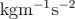 ). Algebraic operations must be performed on these
properties using consistent units of measurement; in particular, addition,
subtraction and equality are only physically meaningful for properties
of the same dimensional units. As a safeguard against implementing a
meaningless operation, OpenFOAM attaches dimensions to field data
and physical properties and performs dimension checking on any tensor
operation.
). Algebraic operations must be performed on these
properties using consistent units of measurement; in particular, addition,
subtraction and equality are only physically meaningful for properties
of the same dimensional units. As a safeguard against implementing a
meaningless operation, OpenFOAM attaches dimensions to field data
and physical properties and performs dimension checking on any tensor
operation.
The I/O format for a dimensionSet is 7 scalars delimited by square brackets, e.g.
[0 2 -1 0 0 0 0]
| No. | Property | SI unit | USCS unit |
| 1 | Mass | kilogram (kg) | pound-mass (lbm) |
| 2 | Length | metre (m) | foot (ft) |
| 3 | Time | second (s) | second (s) |
| 4 | Temperature | Kelvin (K) | degree Rankine ( R) R) |
| 5 | Quantity | mole (mol) | mole (mol) |
| 6 | Current | ampere (A) | ampere (A) |
| 7 | Luminous intensity | candela (cd) | candela (cd) |
where each of the values corresponds to the power of each of the base units of
measurement listed in Table 4.2. The table gives the base units for the Système
International (SI) and the United States Customary System (USCS) but
OpenFOAM can be used with any system of units. All that is required is that
the input data is correct for the chosen set of units. It is particularly
important to recognise that OpenFOAM requires some dimensioned physical
constants, e.g. the Universal Gas Constant 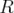 , for certain calculations, e.g.
thermophysical modelling. These dimensioned constants are specified
in a DimensionedConstant sub-dictionary of main controlDict file of the
OpenFOAM installation ($WM_PROJECT_DIR/etc/controlDict). By default these
constants are set in SI units. Those wishing to use the USCS or any other
system of units should modify these constants to their chosen set of units
accordingly.
, for certain calculations, e.g.
thermophysical modelling. These dimensioned constants are specified
in a DimensionedConstant sub-dictionary of main controlDict file of the
OpenFOAM installation ($WM_PROJECT_DIR/etc/controlDict). By default these
constants are set in SI units. Those wishing to use the USCS or any other
system of units should modify these constants to their chosen set of units
accordingly.
4.2.7 Dimensioned types
Physical properties are typically specified with their associated dimensions. These entries formally have the format that the following example of a dimensionedScalar demonstrates:
nu nu [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0] 1;
The majority of dimensioned keyword lookups set a default for the word name which can therefore be omitted from the entry, so the more common syntax is:
nu [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0] 1;
4.2.8 Fields
Much of the I/O data in OpenFOAM are tensor fields, e.g. velocity, pressure data, that are read from and written into the time directories. OpenFOAM writes field data using keyword entries as described in Table 4.3.
| Keyword | Description | Example |
| dimensions | Dimensions of field | [1 1 -2 0 0 0 0] |
| internalField | Value of internal field | uniform (1 0 0) |
| boundaryField | Boundary field | see file listing in section 4.2.8 |
The data begins with an entry for its dimensions. Following that, is the internalField, described in one of the following ways.
- Uniform field
- a single value is assigned to all elements within the field, taking
the form: internalField uniform <entry>;
- Nonuniform field
- each field element is assigned a unique value from a list,
taking the following form where the token identifier form of list is
recommended: internalField nonuniform <List>;
The boundaryField is a dictionary containing a set of entries whose names correspond to each of the names of the boundary patches listed in the boundary file in the polyMesh directory. Each patch entry is itself a dictionary containing a list of keyword entries. The mandatory entry, type, describes the patch field condition specified for the field. The remaining entries correspond to the type of patch field condition selected and can typically include field data specifying initial conditions on patch faces. A selection of patch field conditions available in OpenFOAM are listed in section 5.2.1, section 5.2.2 and section 5.2.3, with a description and the data that must be specified with it. Example field dictionary entries for velocity U are shown below:
18
19 internalField uniform (0 0 0);
20
21 boundaryField
22 {
23 movingWall
24 {
25 type fixedValue;
26 value uniform (1 0 0);
27 }
28
29 fixedWalls
30 {
31 type noSlip;
32 }
33
34 frontAndBack
35 {
36 type empty;
37 }
38 }
39
40 // ************************************************************************* //
4.2.9 Macro expansion
OpenFOAM dictionary files include a macro syntax to allow convenient configuration of case files. The syntax uses the the dollar ($) symbol in front of a keyword to expand the data associated with the keyword. For example the value set for keyword a below, 10, is expanded in the following line, so that the value of b is also 10.
a 10;
b $a;
Variables can be accessed within different levels of sub-dictionaries, or scope. Scoping is performed using a ‘.’ (dot) syntax, illustrated by the following example, where b is set to the value of a, specified in a sub-dictionary called subdict.
subdict
{
a 10;
}
b $subdict.a;
- to traverse up one level of sub-dictionary, use the ‘..’ (double-dot) prefix, see below;
- to traverse up two levels use ‘...’ (triple-dot) prefix, etc.;
- to traverse to the top level dictionary use the ‘:’ (colon) prefix (most useful), see below;
- for multiple levels of macro substitution, each specified with the ‘$’ dollar syntax, ‘{}’ brackets are required to protect the expansion, see below.
a 10;
b a;
c ${${b}}; // returns 10, since $b returns "a", and $a returns 10
subdict
{
b $..a; // double-dot takes scope up 1 level, then "a" is available
subsubdict
{
c $:a; // colon takes scope to top level, then "a" is available
}
}
4.2.10 Including files
There is additional file syntax that provides further flexibility for setting up of OpenFOAM case files, namely directives. Directives are commands that can be contained within case files that begin with the hash (#) symbol. The first set of directive commands are those for reading a data file from within another data file. For example, let us say a user wishes to set an initial value of pressure once to be used as the internal field and initial value at a boundary. We could create a file, e.g. named initialConditions, which contains the following entries:
pressure 1e+05;
In order to use this pressure for both the internal and initial boundary fields, the user would simply include the initialConditions file using the #include directive, then use macro expansions for the pressure keyword, as follows.
#include "initialConditions"
internalField uniform $pressure;
boundaryField
{
patch1
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
}
The file include directives are as follows:
- #include "<path>/<fileName>"
- reads the file of name <fileName> from an absolute or relative directory path <path>;
- #includeIfPresent "<path>/<fileName>"
- reads the file if it exists;
- #includeEtc "<path>/<fileName>"
- reads the file of name <fileName> from the directory path <path>, relative to the $FOAM_ETC directory;
- #includeFunc <fileName>
- reads the file of name <fileName>, searched from the case system directory, followed by the $FOAM_ETC directory;
- #remove <keywordEntry>
- removes any included keyword entry; can take a word or regular expression;
4.2.11 Regular expressions
When running an application, data is initialised by looking up keywords from dictionaries. The user can either provide an entry with a keyword that directly matches the one being looked up, or can provide a POSIX regular expression that matches the keyword, specified inside double-quotations ("…"). Regular expressions have an extensive syntax for various matches of text patterns but they are typically only used in the following ways in OpenFOAM input files.
- "inlet.*" matches any word beginning inlet…, including inlet itself, because ‘.’ denotes “any character” and ‘*’ denotes “repeated any number of times, including 0 times”.
- "(inlet|output)" matches inlet and outlet because () specified an expression grouping and | is an OR operator.
4.2.12 Keyword ordering
The order in which keywords are listed does not matter, except when the same keyword is specified multiple times. Where the same keyword is duplicated, the last instance is used. The most common example of a duplicate keyword occurs when a keyword is included from the file or expanded from a macro, and then overridden. The example below demonstrates this, where pFinal adopts all the keyword entries, including relTol 0.05 in the p sub-dictionary by the macro expansion $p, then overrides the relTol entry.
p
{
solver PCG;
preconditioner DIC;
tolerance 1e-6;
relTol 0.05;
}
pFinal
{
$p;
relTol 0;
}
Where a data lookup matches both a keyword and a regular expression, the keyword match takes precedence irrespective of the order of the entries.
4.2.13 Inline calculations and code
There are two further directives that enable calculations from within input files: #calc, for simple calculations; #codeStream, for more complex calculations.
The pipeCyclic tutorial in $FOAM_TUTORIALS/incompressible/simpleFoam demonstrates the #calc directive through its blockMesh configuration in blockMeshDict:
//- Half angle of wedge in degrees
halfAngle 45.0;
//- Radius of pipe [m]
radius 0.5;
radHalfAngle #calc "degToRad($halfAngle)";
y #calc "$radius*sin($radHalfAngle)";
minY #calc "-1.0*$y";
z #calc "$radius*cos($radHalfAngle)";
minZ #calc "-1.0*$z";
The #codeStream directive takes C++ code which is compiled and executed to deliver the dictionary entry. The code and compilation instructions are specified through the following keywords.
- code: specifies the code, called with arguments OStream& os and const dictionary& dict which the user can use in the code, e.g. to lookup keyword entries from within the current case dictionary (file).
- codeInclude (optional): specifies additional C++ #include statements to include OpenFOAM files.
- codeOptions (optional): specifies any extra compilation flags to be added to EXE_INC in Make/options.
- codeLibs (optional): specifies any extra compilation flags to be added to LIB_LIBS in Make/options.
Code, like any string, can be written across multiple lines by enclosing it within hash-bracket delimiters, i.e. #{…#}. Anything in between these two delimiters becomes a string with all newlines, quotes, etc. preserved.
An example of #codeStream is given below, where the code in the calculates moment of inertia of a box shaped geometry.